EMG (Electromyography)
EMG is a diagnostic test that evaluates the health of muscles and the motor neurons (nerves that control muscles). It helps detect neuromuscular abnormalities and determine the cause of muscle weakness.
What EMG Does:
- Measures electrical activity in muscles at rest and during contraction
- Determines if muscle weakness is caused by muscle or nerve problems
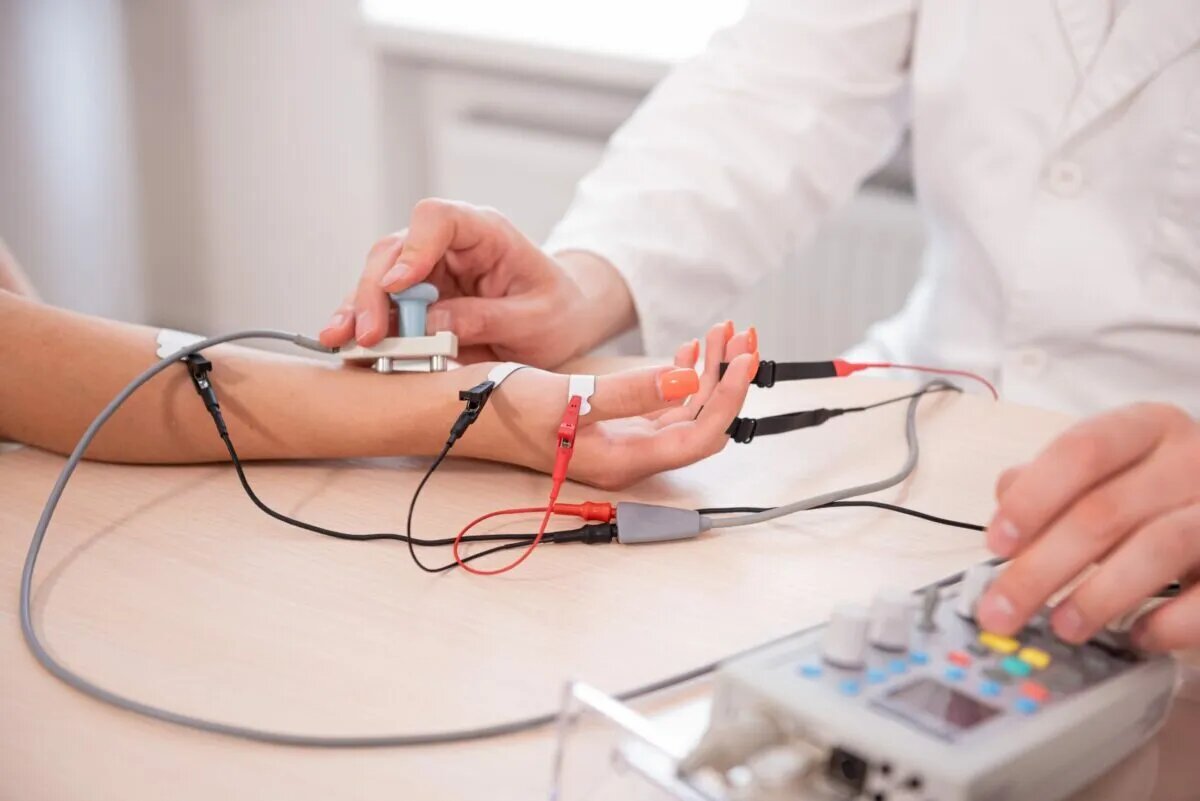
How EMG Works
Recording muscle and nerve electrical activity
Electrode Placement
Small needle with electrode inserted into muscle tissue
Rest Recording
Records electrical activity when muscle is at rest
Contraction Recording
Records activity during muscle contraction
Analysis
Neurologist analyzes patterns for abnormalities
What EMG Measures
Comprehensive neuromuscular assessment
Electrical Activity at Rest
Records muscle activity when completely relaxed
Electrical Activity During Contraction
Records activity when muscle is being used
Motor Nerve Function
Assesses how nerves control muscles
Muscle vs Nerve Problems
Determines source of muscle weakness
When Is EMG Used?
Common diagnoses made with EMG testing
Neuropathies
Nerve damage and dysfunction
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Nerve entrapment
Radiculopathies
Nerve root compression or irritation
- Pinched nerve in spine
- Cervical radiculopathy
- Sciatica
- Nerve compression
Myopathies
Muscle disorders and diseases
- Muscular dystrophy
- Polymyositis
- Dermatomyositis
- Muscle inflammation
Motor Neuron Diseases
Diseases affecting nerve-muscle connection
- ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)
- Polio
- Myasthenia gravis
- Progressive weakness
Advantages of EMG Testing
Accurate neuromuscular diagnosis
Definitive Diagnosis
Identifies nerve and muscle disorders accurately
Distinguishes Causes
Determines if weakness is from muscle or nerve
Disease Monitoring
Tracks progression of neuromuscular conditions
Outpatient Procedure
No hospitalization required, same-day discharge
Minimally Invasive
Small needle insertion with minimal discomfort
Quick Results
Takes 30-60 minutes with immediate analysis
Conditions Diagnosed by EMG
Wide range of neuromuscular disorders
Is EMG Painful?
During the Test:
Slight Discomfort
When the needle electrode is inserted into the muscle
Mild Sensation
May feel slight tingling or muscle twitching
After the Test:
Mild Soreness
Tested muscles may feel sore for a few days
Minor Bruising
Small bruises may appear at needle insertion sites
Tip: Discomfort is usually minimal and manageable. Tell your neurologist if you need a break during the procedure. Most patients tolerate the test well, and any soreness typically fades within a few days.
How to Prepare for EMG
Important guidelines for accurate testing
Your EMG Test Journey
From preparation to analysis
Preparation
Skin cleaned and site prepared
Nerve Conduction Study
Surface electrodes applied first
Needle EMG
Needle electrodes inserted into muscle
Analysis
Neurologist reviews recorded data

