NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity)
NCV (Nerve Conduction Velocity) is a medical diagnostic test used to evaluate the function of peripheral nerves—especially to detect nerve damage or dysfunction.
Purpose:
Measures how fast electrical signals move through your peripheral nerves
Commonly Diagnoses:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Peripheral neuropathy (especially diabetic)
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Radiculopathies (e.g., slipped disc)
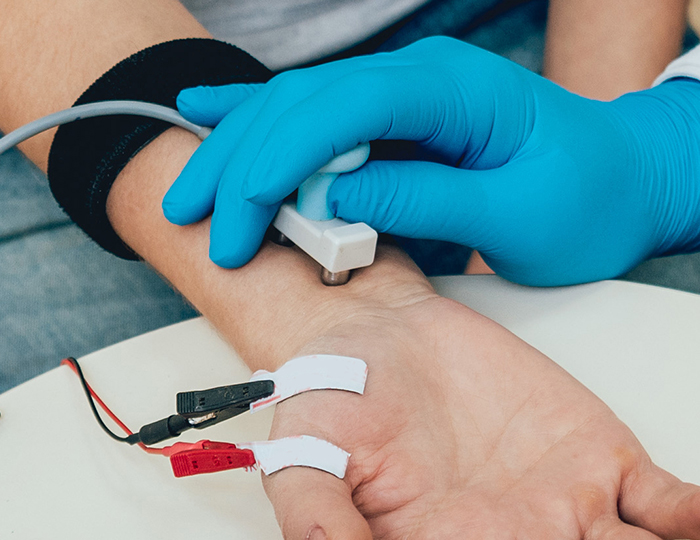
How NCV Test Works
Measuring peripheral nerve function
Electrode Placement
Surface electrodes are placed on skin over a nerve
Electrical Stimulation
Small electrical pulse is applied to stimulate the nerve
Signal Detection
Sensors detect the signal traveling through the nerve
Velocity Measurement
Speed and strength of nerve signal are calculated
In healthy nerves: Electrical signals can travel up to 120 miles per hour. If your nerve is damaged, the current will be slower and weaker. By stimulating the nerve at various places, the provider can determine the specific site of nerve injury.
What Does NCV Measure?
Comprehensive peripheral nerve assessment
Signal Speed
How fast electrical signals move through nerves
Signal Strength
Amplitude and quality of nerve signals
Nerve Function
Overall nerve health and conduction capability
Damage Detection
Identifies location and extent of nerve injury
Commonly Used For Diagnosing
Key peripheral nerve disorders
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Nerve compression in the wrist
- Median nerve compression
- Wrist nerve damage
- Hand numbness/tingling
- Compression severity assessment
Peripheral Neuropathy
Nerve damage, commonly in diabetes
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Nerve fiber damage
- Sensory/motor nerve testing
- Disease progression monitoring
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Auto-immune nerve disorder
- Acute demyelination
- Ascending paralysis
- Nerve conduction abnormality
- Immune-mediated nerve damage
Radiculopathies
Nerve root compression or irritation
- Slipped disc
- Nerve root compression
- Spinal stenosis
- Root compression severity
Advantages of NCV Testing
Accurate peripheral nerve assessment
Non-Invasive
No needles or surgical procedures
Painless Test
Mild tingling sensation, no real pain
Quick Procedure
Takes 15 minutes to 1 hour depending on nerves tested
Precise Diagnosis
Accurately identifies nerve damage and dysfunction
Safe & Effective
Minimal risks with high diagnostic accuracy
Outpatient Service
No hospitalization required
Conditions Diagnosed by NCV
Wide range of peripheral nerve disorders
How to Prepare for NCV Test
Important guidelines for accurate testing
Your NCV Test Journey
Step-by-step nerve conduction testing
Preparation
Body warming and electrode placement
Recording Electrode
Placed on muscles controlled by nerves
Stimulation
Mild electrical pulses applied to nerves
Analysis
Neurologist records conduction velocity
Frequently Asked Questions
Book Your NCV Test Today
Accurate peripheral nerve function assessment for nerve disorders diagnosis

